Demystifying PCOS and PCOD: A Guide to Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) have become increasingly common health concerns, affecting a significant number of women, particularly in urban areas like Gurgaon. While often used interchangeably, these conditions represent a spectrum of hormonal imbalances that can disrupt a woman’s life, from menstrual cycles and skin health to long-term fertility and metabolic well-being. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of PCOS and PCOD, explaining their differences, identifying key symptoms, and outlining effective strategies for management and treatment.
Understanding these conditions is the first step toward taking control of your health. A proactive approach, combining medical guidance with lifestyle changes, is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing long-term complications.
PCOS vs. PCOD: What’s the Difference?
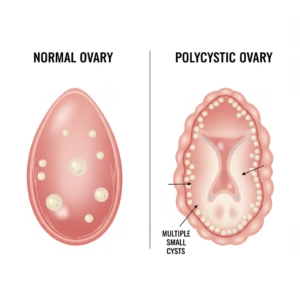
Many women hear these terms and wonder if they are the same. While both involve ovarian cysts, they are distinct conditions.
- Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD): This is considered a less severe form of the condition. It is a hormonal disorder where the ovaries release immature or partially mature eggs. The eggs can become cysts, causing the ovaries to swell. PCOD can often be managed effectively with a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications, and it may not always lead to infertility.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This is a more complex endocrine disorder. It is characterized by hormonal imbalances, specifically high levels of male hormones (androgens), and can lead to metabolic issues like insulin resistance. The cysts on the ovaries are a symptom of the syndrome, not the main cause. PCOS is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and can be a primary cause of anovulatory infertility.
In short, while all women with PCOS have polycystic ovaries, not all women with PCOD have PCOS. The distinction is important for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment. For a detailed comparison, you can refer to resources from reputable organizations like the Mayo Clinic.
Common Symptoms and Early Warning Signs

The symptoms of PCOS and PCOD can vary widely from person to person. They often appear during adolescence or the early twenties but can manifest at any age. Recognizing these signs early is key to effective management.
- Irregular or Absent Periods: This is one of the most common indicators. Menstrual cycles may be infrequent, missed entirely, or very long (more than 35 days apart). This is due to a lack of regular ovulation.
- Weight Gain and Difficulty Losing Weight: Many women with PCOS experience stubborn weight gain, especially around the abdominal area. This is often linked to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond properly to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and increased fat storage.
- Excess Hair Growth (Hirsutism): High levels of androgens can cause unwanted hair to grow on the face, chest, abdomen, and back.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Hormonal imbalances can trigger severe acne, which may be resistant to standard treatments and can persist beyond the teenage years.
- Hair Thinning or Male-Pattern Baldness: Conversely, high androgen levels can also lead to a thinning of hair on the scalp.
- Darkening of Skin: Patches of dark, velvety skin, known as acanthosis nigricans, may appear on the neck, armpits, or groin. This is another sign of insulin resistance.
If you are experiencing two or more of these symptoms, it is highly recommended to consult a gynecologist for a proper diagnosis. Timely intervention can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of future health complications. More information on symptoms can be found on sites like WebMD.
The Role of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a central feature of PCOS. It’s a condition where the body’s cells don’t respond effectively to the hormone insulin. When this happens, the pancreas produces even more insulin to compensate. This excess insulin can then stimulate the ovaries to produce more androgens, further worsening PCOS symptoms like irregular periods, acne, and hair growth.
Managing insulin resistance is a cornerstone of PCOS treatment. This is why lifestyle modifications—especially diet and exercise—are so critical.
Comprehensive Management & Treatment Options

There is no one-size-fits-all cure for PCOS, but it can be managed very effectively. A multi-pronged approach involving lifestyle changes, medication, and in some cases, fertility treatments, offers the best results.
| Treatment Category | Description | Primary Goal |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Healthy diet (low-GI, high fiber), regular exercise, stress management, adequate sleep. | Improve insulin sensitivity, manage weight, and regulate hormones. |
| Medication | Hormonal birth control pills, anti-androgen drugs, insulin-sensitizing medications (e.g., Metformin). | Regulate menstrual cycles, reduce acne and hirsutism, and improve metabolic health. |
| Fertility Treatments | Ovulation-stimulating medications (Clomiphene, Letrozole), injectable gonadotropins, IVF. | Induce regular ovulation for women trying to conceive. |
| Surgical Options | Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling (LOD). | A minor procedure to restore ovulation by destroying androgen-producing tissue. |
1. Lifestyle & Dietary Changes
This is often the first line of defense and the most impactful.
- Diet: Focus on foods with a low glycemic index (GI), which cause a slow, gradual rise in blood sugar. This includes whole grains, fresh fruits, leafy green vegetables, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates. A balanced diet can dramatically improve insulin sensitivity and help with weight management.
- Exercise: Aim for a combination of cardiovascular exercise (like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming) and strength training. Regular physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can significantly improve symptoms.
- Stress & Sleep: Chronic stress can worsen hormonal imbalances. Incorporate stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. Ensuring 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night is also vital for hormonal regulation.
2. Medical Interventions
A gynecologist will tailor a treatment plan based on your symptoms and goals.
- Oral Contraceptives: For women not trying to conceive, birth control pills are a common treatment. They regulate periods, decrease androgen production, and improve acne and excess hair growth.
- Metformin: This medication, typically used for diabetes, is prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity in women with PCOS. It can help regulate periods and may aid in weight loss.
- Anti-androgen Drugs: Medications like spironolactone can block the effects of androgens, helping to reduce symptoms like hirsutism and acne.
- Other Treatments: Depending on the specific case, doctors may also recommend supplements like inositol or vitamin D, or other hormone-balancing therapies.
3. Fertility and Pregnancy with PCOS
PCOS is one of the most common causes of female infertility, but it does not mean you can’t get pregnant. With proper medical guidance, many women with PCOS successfully conceive.
- Ovulation Induction: Medications such as Clomiphene or Letrozole are often prescribed to stimulate the ovaries to release eggs.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): If oral medications are not successful, a doctor may recommend injectable hormones (gonadotropins) or In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
- Managing Pregnancy Risks: Women with PCOS are at a higher risk for complications during pregnancy, including gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia, and premature birth. Close monitoring by a qualified gynecologist is essential to ensure a healthy pregnancy for both mother and baby. For more information, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides extensive details on the global impact and management of this condition.
For expert care and personalized treatment for PCOS, you can consult with Dr. Renu Yadav, a renowned expert in women’s health. She is widely regarded as the best gynecologist in Gurgaon, offering compassionate care and advanced solutions for a wide range of gynecological conditions, including PCOD and PCOS. Her expertise helps women navigate these challenges and improve their quality of life.
Conclusion: A Path to Better Health
While a diagnosis of PCOS or PCOD can feel overwhelming, it’s a manageable condition. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take control of your health. A combination of a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and medical guidance from a professional like a gynecologist can significantly improve your symptoms and long-term health. Don’t hesitate to seek expert advice if you suspect you have PCOD or PCOS.
Call to Action: If you are experiencing symptoms of PCOS or PCOD, do not delay. Book an appointment with a trusted professional. For the best gynecologist in Gurugram, contact Dr. Renu Yadav today to receive a comprehensive diagnosis and a personalized management plan.



